 White et al. 2019
White et al. 2019Resumen
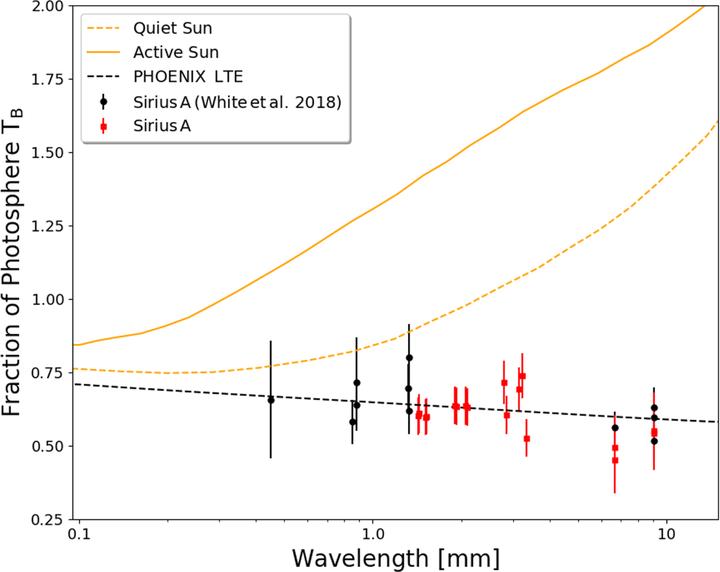
Modeling the submillimeter to centimeter emission of stars is challenging due to a lack of sensitive observations at these long wavelengths. We launched an ongoing campaign to obtain new observations entitled Measuring the Emission of Stellar Atmospheres at Submillimeter/millimeter wavelengths (MESAS). Here we present Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, Green Bank Telescope, and Very Large Array observations of Sirius A, the closest main-sequence A-type star, that span from 1.4 to 9.0 mm. These observations complement our previous millimeter data on Sirius A and are entirely consistent with the PHOENIX stellar atmosphere models constructed to explain them. We note that accurate models of long-wavelength emission from stars are essential not only to understand fundamental stellar processes, but also to determine the presence of dusty debris in spatially unresolved observations of circumstellar disks.